epidemiology

New York Flu Watch: Real-Time Tracking and Analysis of Influenza Data
March 28, 2025
communicable diseases data visualization epidemiology influenza New York State Public Health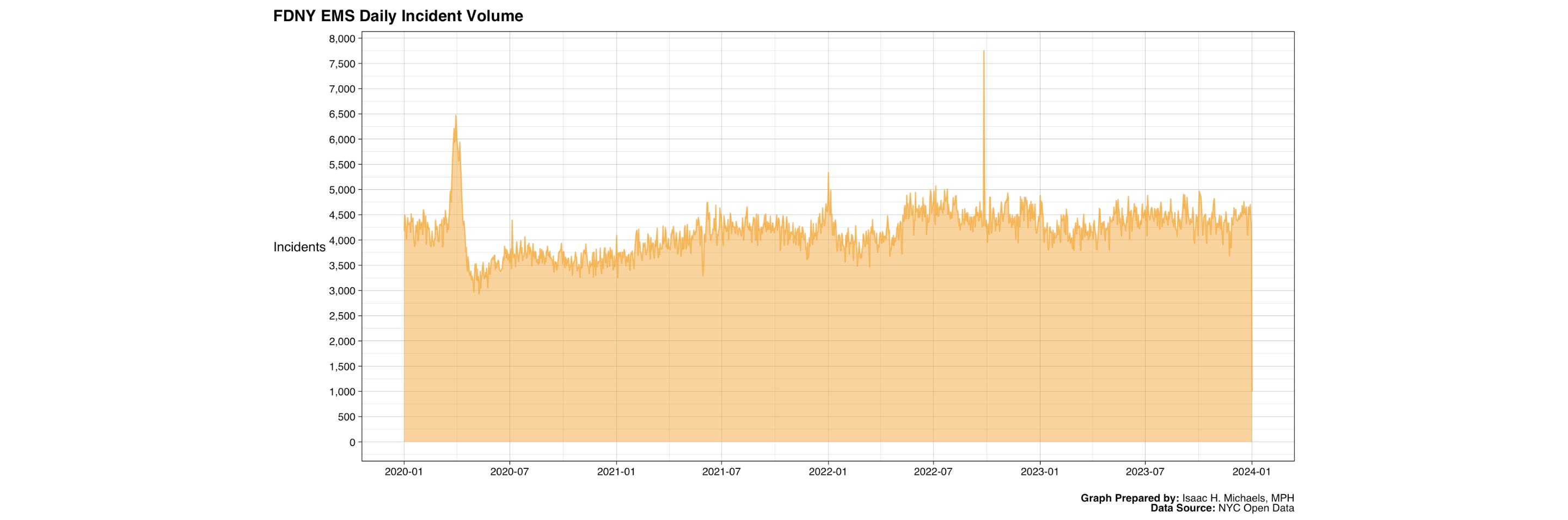
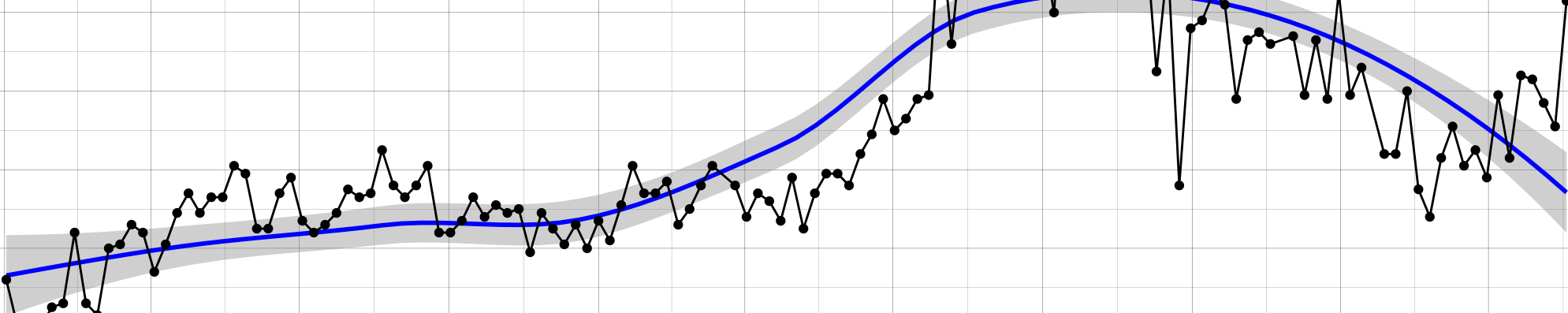
EMS Calls in New York City: Trends and Patterns
February 18, 2025
EMS epidemiology NYC health care delivery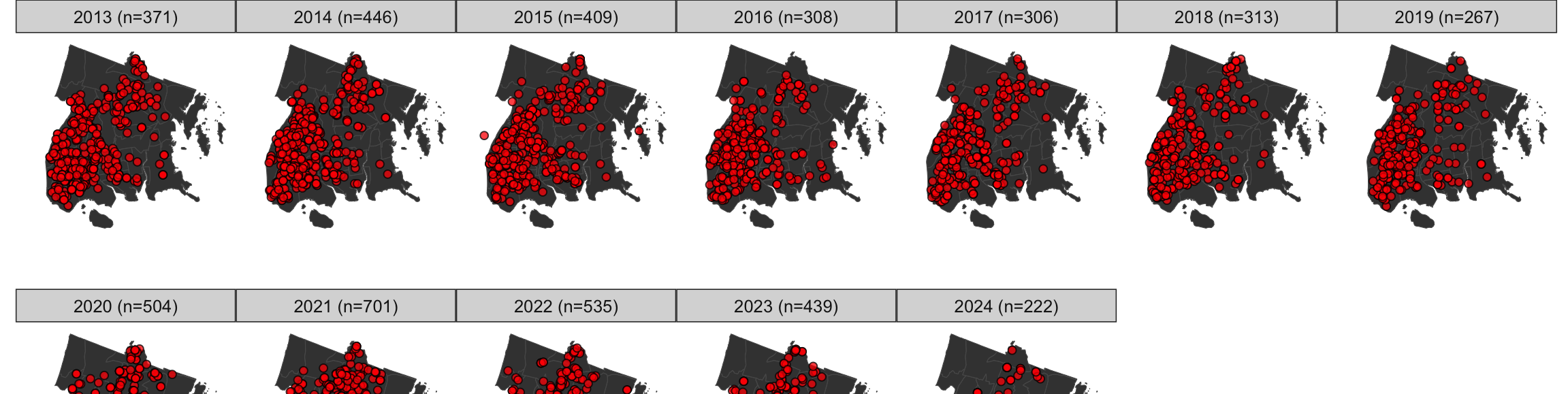
Shooting Incidents in New York City
January 27, 2025
gun violence GIS epidemiology NYC Public Health Crime Trends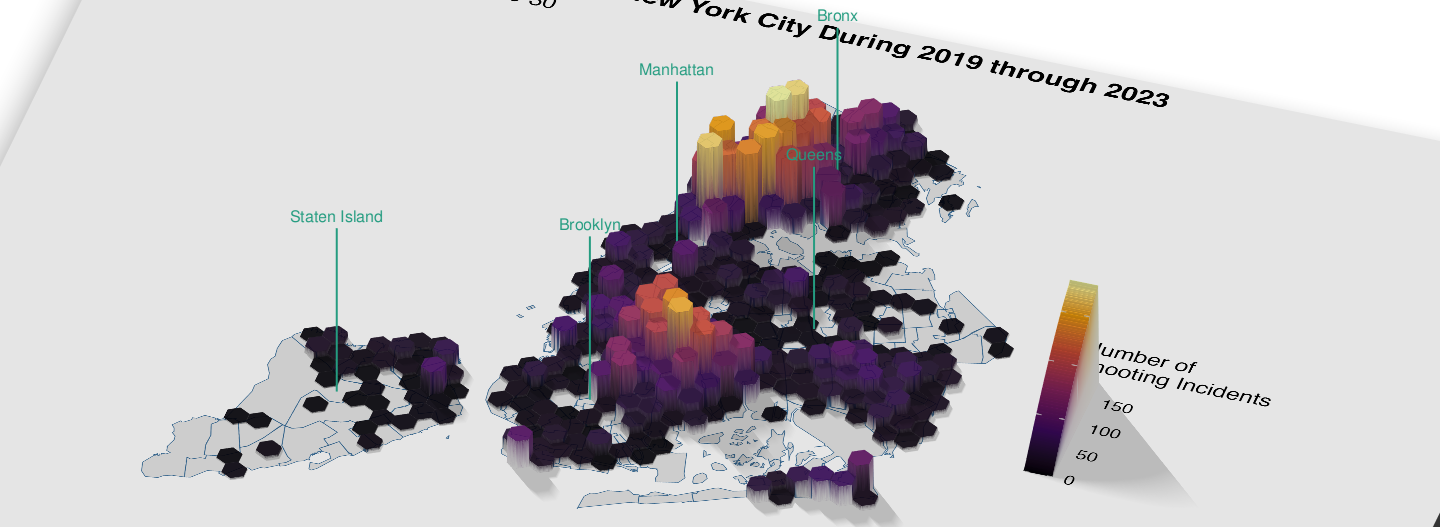
Using Three-Dimensional Mapping to Visualize Five Years of Shooting Incidents in New York City
August 20, 2024
Gun Violence New York City Three-dimensional mapping Public Health GIS epidemiology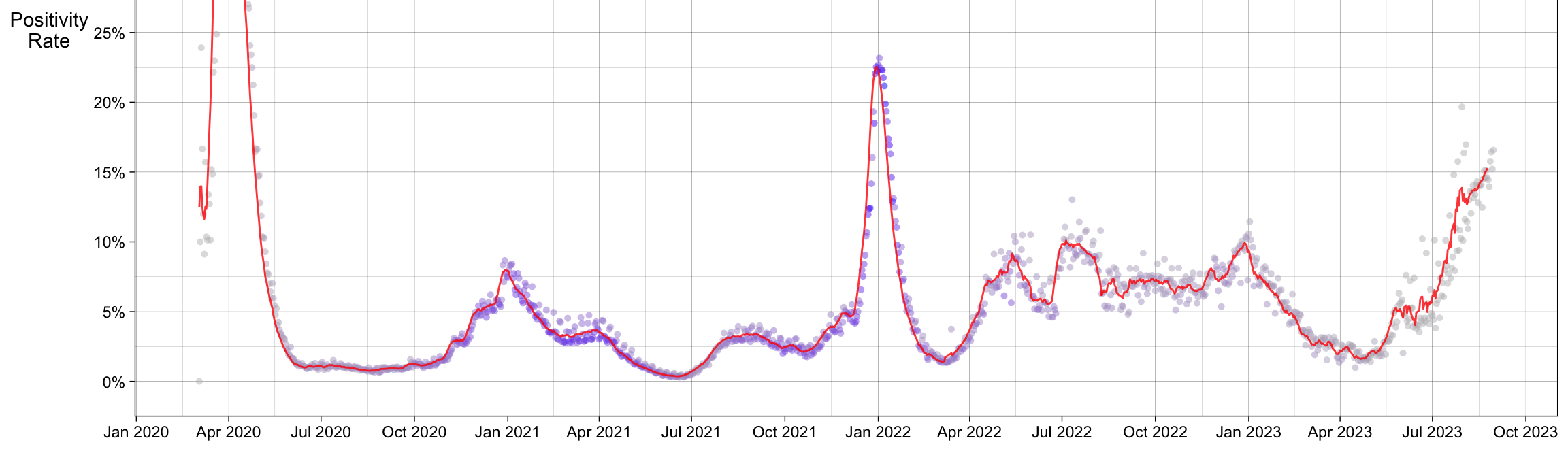
New York COVID-19 Data Tracking Report
March 30, 2025
COVID-19 GIS epidemiology communicable diseases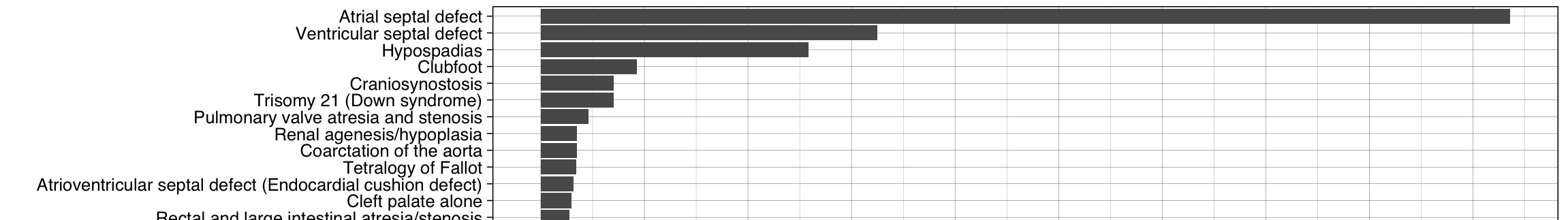
Birth Defect Trends in New York State
December 31, 2024
birth defects maternal and child health epidemiology public health New York State disease incidence epidemiology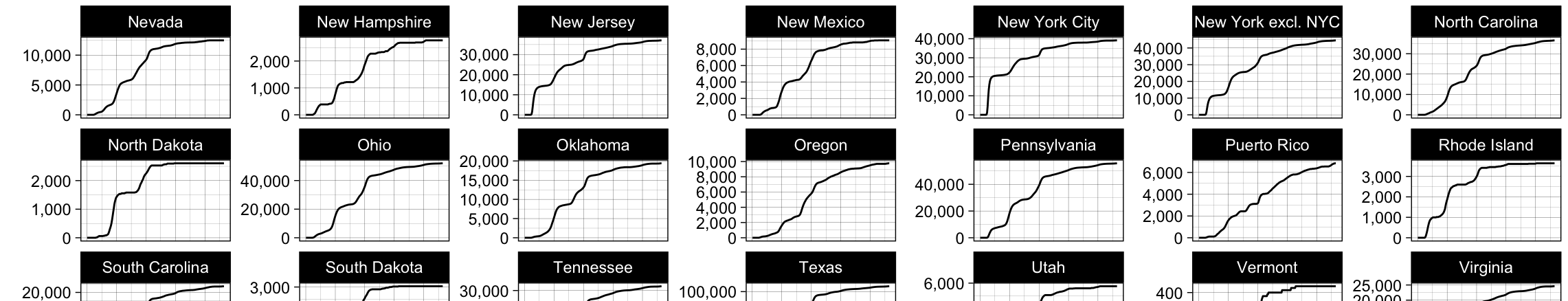
United States COVID-19 Data Tracking Report
March 31, 2025
COVID-19 epidemiology GIS communicable diseases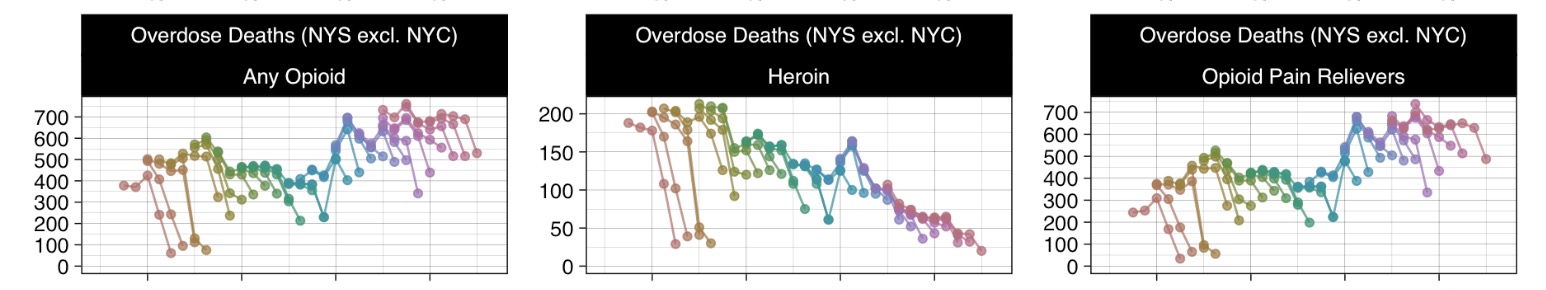
Opioid Overdoses in New York (Provisional Data)
January 25, 2025
data visualization epidemiology New York State opioids overdose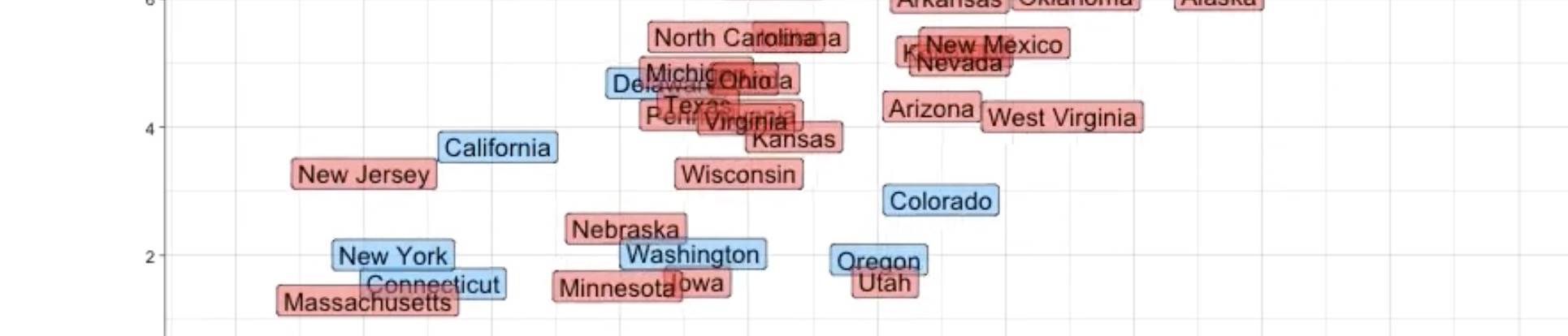
Universal Background Checks and Firearm Mortality in States
September 2, 2024
gun violence epidemiology data visualization policyInfluenza Vaccination Among New York Healthcare Workers
February 18, 2024
health care delivery New York State influenza immunization patient safety epidemiology communicable diseasesUnited States Weekly Death by Select Causes (2014 to Present)
November 14, 2023
data visualization epidemiology United States Public HealthNew York Weekly Death by Select Causes (2014 to Present)
November 14, 2023
data visualization epidemiology New York State Public HealthCOVID-19 Predictions for New York State
September 7, 2023
epidemiology COVID-19 communicable diseases New York State data science predictive modeling machine learning Public Health PracticeAnalysis of Immunization Levels Among Schools in New York State
September 1, 2023
epidemiology data visualization immunization New York State vaccine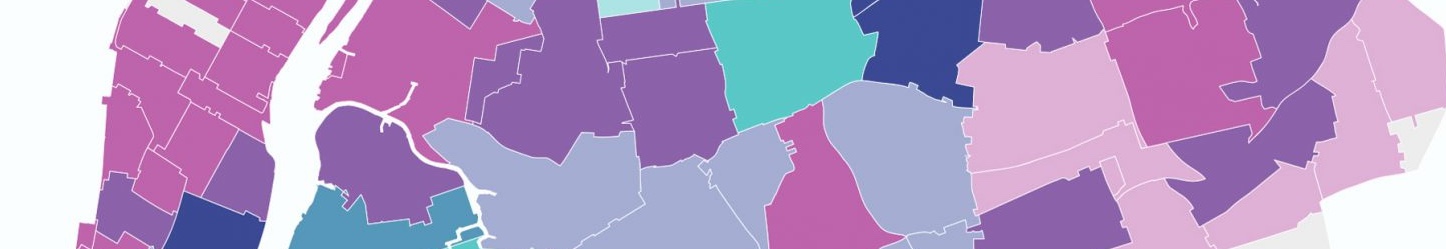
Research Team Uncovers Disparities in Internet Access and COVID-19 Vaccination in New York City
August 26, 2021
COVID-19 epidemiology New York City GIS Public Health Social Determinants immunization
New Publication Outlines Methods for Generating Subcounty Health Data
April 17, 2020
Small-Area Data epidemiology Health Disparities community health needs assessment
Food Distress Linked to Smoking in Racially and Ethnically Diverse Adults
August 24, 2017
chronic disease Community Health environemental health Health Disparities epidemiology environment Public Health Practice Social Determinants
Tobacco Availability and Advertising Decrease in Albany, NY Food Stores
May 12, 2016
Albany NY Tobacco Control environemental health Public Health Social Determinants epidemiology Community Health chronic disease
Study Examines the Impact of Food Shopping Venues and Neighborhood Food Environment on BMI in Urban Adults
April 16, 2016
Community Health chronic disease environemental health epidemiology Health Disparities Public Health
New Study Finds Travel Distance Poses Barrier to Participation in Diabetes Intervention Programs for Guyanese Immigrants at Faith-Based Organizations
May 8, 2014
Public Health GIS chronic disease Diabetes data visualization environment epidemiology Social Determinants